
This will be your router’s IP address on your local network.

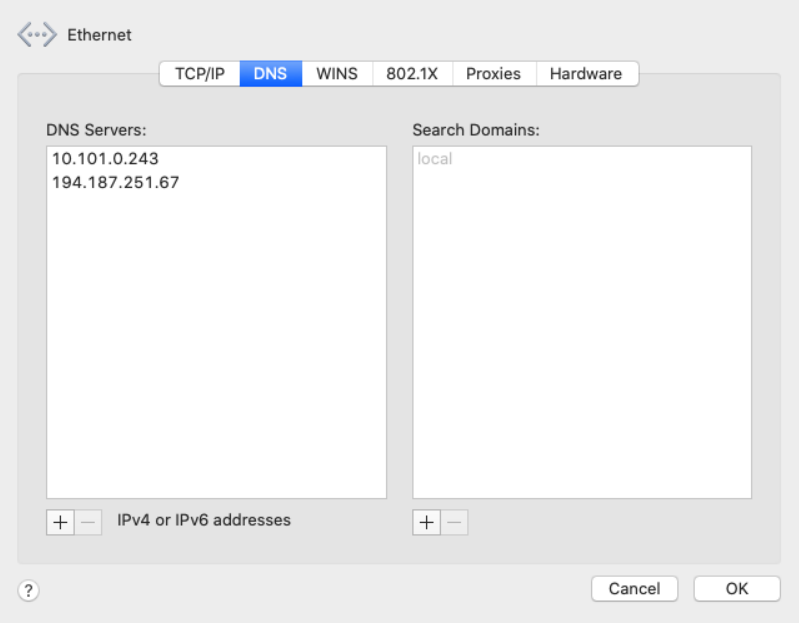
In the example above, it’s 8.8.8.8.īe aware that in many home networking configurations, you will likely see an IP address starting .X or 10.X.X.X. The line starting “Address” will show your DNS server.You’ll see results that look like these:Īddress: 8.8.8.8 Non-authoritative answer:.On Windows, open the Command Prompt by: clicking ‘Start Menu,’ typing cmd, and pressing ‘Enter.’ On Mac, open the Terminal by: pressing the Command Key + Space Bar, typing terminal, then pressing ‘Enter.’.Here is how to find your DNS server on PC or Mac step-by-step: We will use a standard utility that takes a domain name as input, and makes a DNS query to resolve that domain name to an IP address. The quickest way to find your DNS server’s IP address on your PC or Mac device is to: Once your web browser knows the IP address of a website, it communicates with the server at the IP address, and displays the received web content that is available on the URL.ĭespite the number of steps involved, the process of resolving a DNS query and displaying a website’s content happens very quickly. This information is then returned to your browser running on your computer. Finally, the resolver communicates with these Authoritative Name Servers, querying the fully-qualified domain name, and receives 1 or more IP addresses which are the servers that host the content required.

The response to this is 1 or more IP addresses for TLD servers. First, the resolver communicates with a DNS Root Server, to find out which servers hold information for the Top-Level Domain (TLD) part of your DNS query, e.g.com or.When the DNS resolver receives such a query, it communicates with several types of servers in a chain to find out which DNS server holds the information to answer the query. When you visit a URL (a website address) in your browser, your device sends a DNS query to the DNS resolvers it knows about via your device’s network settings, and the DNS resolver responds with the IP addresses on the internet where that website is located.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
